All About Launching mysql(or Similar Image) on docker

One of the basic requirement to start project these days is to spool a docker and start working especially for databases.The is point to point guide on how to do the same.
If you want one line code go here
Pre-Requisites
- Basic understanding on docker especially about Images and Containers
- sql CRUD commands
- docker installed on your system
NOTE : in case you want to jump straight to the code here
Pull the Image from Docker Hub
First get the Image from docker hub
docker pull mysql/mysql-server:latest
Now Check whether the Image is available , and the response would be similar to one given below
docker images

Deploy the Image
Run the following command , here
- -d : means to run image as service
- ‘latest’ tag can be replaced with the custom as well (in case you want to install some other version)
- [container_name] : this is custom name that you want to provide
docker run --name=[container_name] -d mysql/mysql-server:latest
Check the status of docker image whether its running with following command
docker ps

Connect to MySql
Make sure the mysql client is present (for linux)
apt-get install mysql-client
to start mysql client inside container use following command
docker exec -it [container_name] mysql -uroot -p
this will prompt password

To get the password , as we have not manually provided , we need to refer to the mysql logs , hence type following command and it will show GENERATED ROOT PASSWORD as shown below
docker logs [container_name]
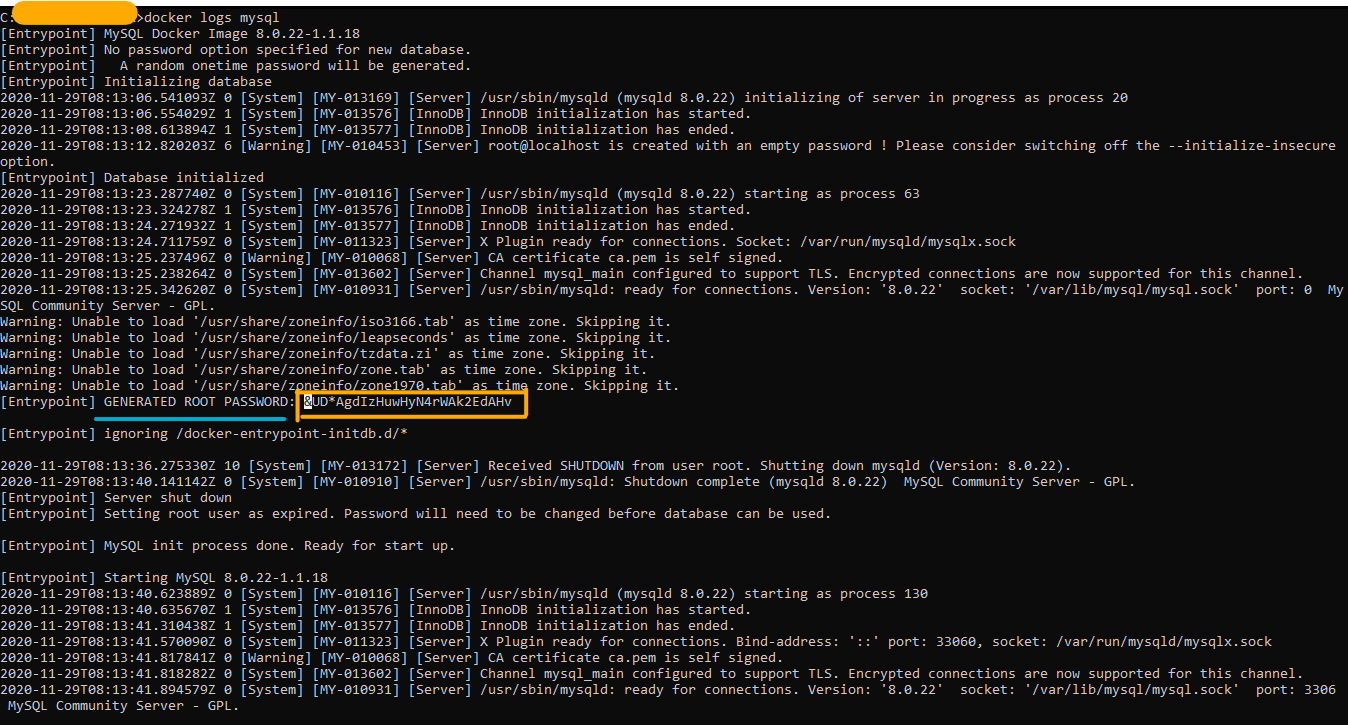
this will open sql window , now we should not want to use Auto Generated mysql and trigger our own password
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '[newpassword]';
Storage
By default docker would be storing all Information inside the docker container
To make it available in host system
docker run --name <Custom_container_name> -v <host_directory_address>:<docker_directory_to_host> -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=<custom_Password> -d mysql:latest
hence one example would be (assuming D:\mySqlData folder is present)
docker run --name mysql-v3 -v D:\mySqlData:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=mypass -d mysql:latest
Operation on Docker
basic operation are to start, stop and restart container
docker start [container_name]
docker stop [container_name]
docker restart [container_name]
Conclusion
Now for mostly your local development one can directly connect to this docker.
After following all above steps you should have been able to successfully connect and deploy a Mysql container
Do Reach out in comment section in case you are facing some issue in any of the steps
References
http://www.ethernetresearch.com/docker/docker-tutorial-persistent-storage-volumes-and-stateful-containers/ https://severalnines.com/database-blog/mysql-docker-containers-understanding-basics
